Understanding Appendicitis
Causes and Treatments Explained
Discover the underlying causes of Appendicitis and explore effective treatment methods to manage and prevent it.
Understanding Appendicitis
As of recent estimates, appendicitis affects approximately 7-8% of the global population at some point in their lives. Each year, about 100 out of every 100,000 people worldwide are diagnosed with acute appendicitis, making it one of the most common surgical emergencies.
What is Appendicitis?
Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix, a small finger-shaped pouch attached to the colon on the right side of the abdomen. The appendix does not have a known function, and one can live without it.
When it occurs, the first symptom is usually pain in the lower abdomen, often starting around the navel and gradually moving to the lower right side. As the inflammation worsens, the pain increases to becomes severe.
This condition can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender, but it is most common in people aged 10 to 30. If the pain becomes severe, surgery is typically needed to remove the appendix.
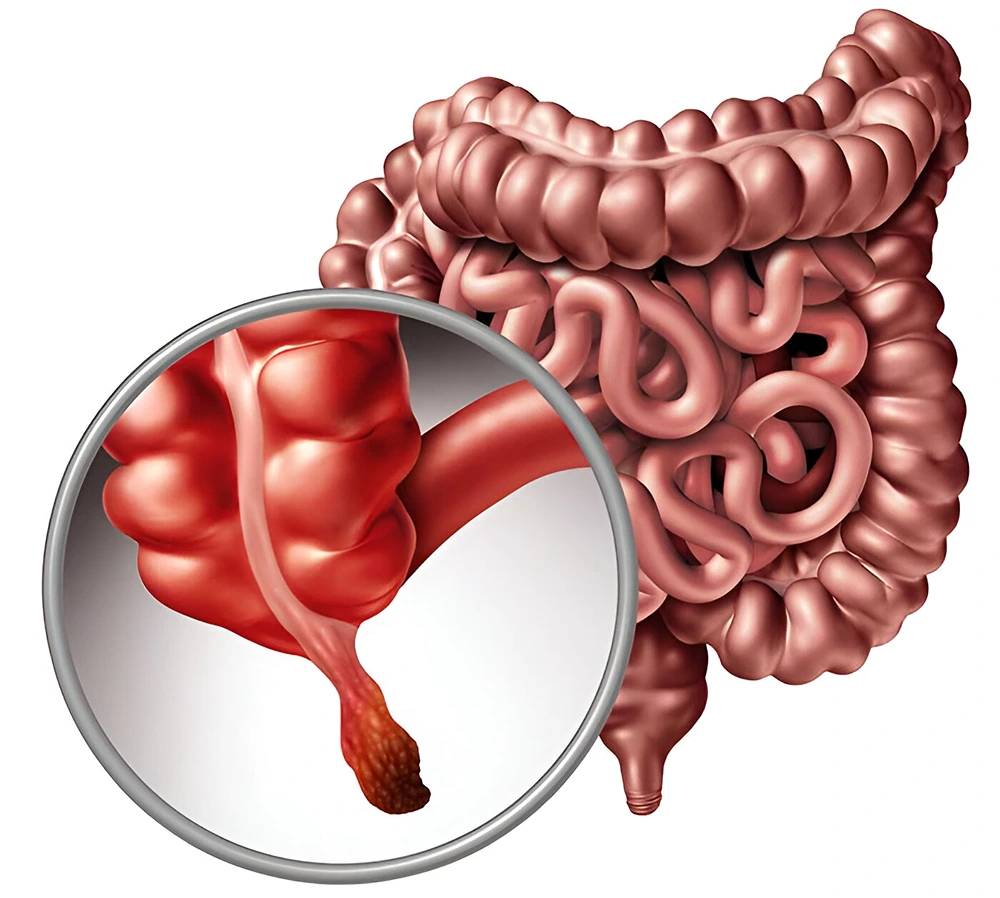
When Does Appendicitis Happen?
Complications of Appendicitis
Symptoms & Treatment of Appendicitis
Symptoms of Appendicitis
Being aware of the symptoms of appendicitis is crucial:
-
Abdominal Pain: Pain in the lower right side of the abdomen is the most common symptom, starting around the belly button and quickly moving to the right side.
-
Increased Pain: Activities such as bumpy rides, coughing, or sneezing exacerbate discomfort associated with appendicitis.
-
Fever and Chills: These symptoms often accompany severe stomach pain, which can be mistaken for a common fever or food poisoning. If fever occurs alongside intense abdominal pain, it’s advisable to seek medical evaluation for possible appendicitis.
-
Digestive Issues: Persistent diarrhea with noticeable amounts of mucus lasting more than 2-3 days suggests potential appendicitis rather than a typical stomach infection.
-
Gas and Bloating: While gas is common with dietary issues, increased pain and persistent bloating may indicate appendicitis.
-
Abdominal Tenderness: Pressing on the abdomen and experiencing pain upon release can indicate appendicitis, necessitating prompt medical attention.
-
Concerning Pain Relief: If pain suddenly diminishes, it may signal a ruptured appendix, requiring urgent medical evaluation to avoid complications.
Treatment of Appendicitis
Diagnosis of Appendicitis – Diagnosing appendicitis typically involves:
- History: Gathering information about symptoms, medical history, and recent events.
- Physical Examination: Checking for signs of tenderness, abdominal rigidity, and rebound tenderness.
- Abdominal Ultrasound: Using sound waves to create images of the appendix and surrounding area.
- Abdominal CT Scan: Providing detailed cross-sectional images to confirm diagnosis and assess for complications like abscesses.
Appendicitis Treatment – In uncomplicated cases:
- Appendectomy: Surgery to remove the appendix is the standard treatment. This procedure is often performed laparoscopically through small incisions, resulting in faster recovery times.
If complications such as an abscess are present:
- Treatment of Infection: Antibiotics are administered to treat the infection and inflammation before surgery.
- Delayed Appendectomy: The appendix is removed once the infection has been controlled, reducing the risk of complications during surgery.
Both approaches aim to prevent the appendix from rupturing or spreading infection, ensuring prompt recovery and minimal post-operative complications. Early diagnosis and timely intervention are crucial for successful treatment of appendicitis.
Get Expert Help Today
Don’t let appendicitis interfere with your life. Contact Max Stone & Surgical Center – Max Hospital Faridabad – for a comprehensive consultation and personalized treatment plan. Our expert team is committed to delivering exceptional care and assistance. Book your appointment now and start your journey towards a healthier, pain-free future.

Get a Call for Appointment
Fill out this form to receive a call from us and schedule your appointment. Start your journey to better health with our expert care today!
