Understanding Enlarged Prostate
Causes and Treatments Explained
Discover the underlying causes of Enlarged Prostate and explore effective treatment methods to manage and prevent it.
Understanding Enlarged Prostate
Enlarged prostate, affects up to 50% of men by age 60 and 90% by age 85 worldwide. It significantly impacts quality of life with symptoms like urinary urgency and nocturia, varying in prevalence across regions and ethnicities, and presenting a substantial healthcare burden.
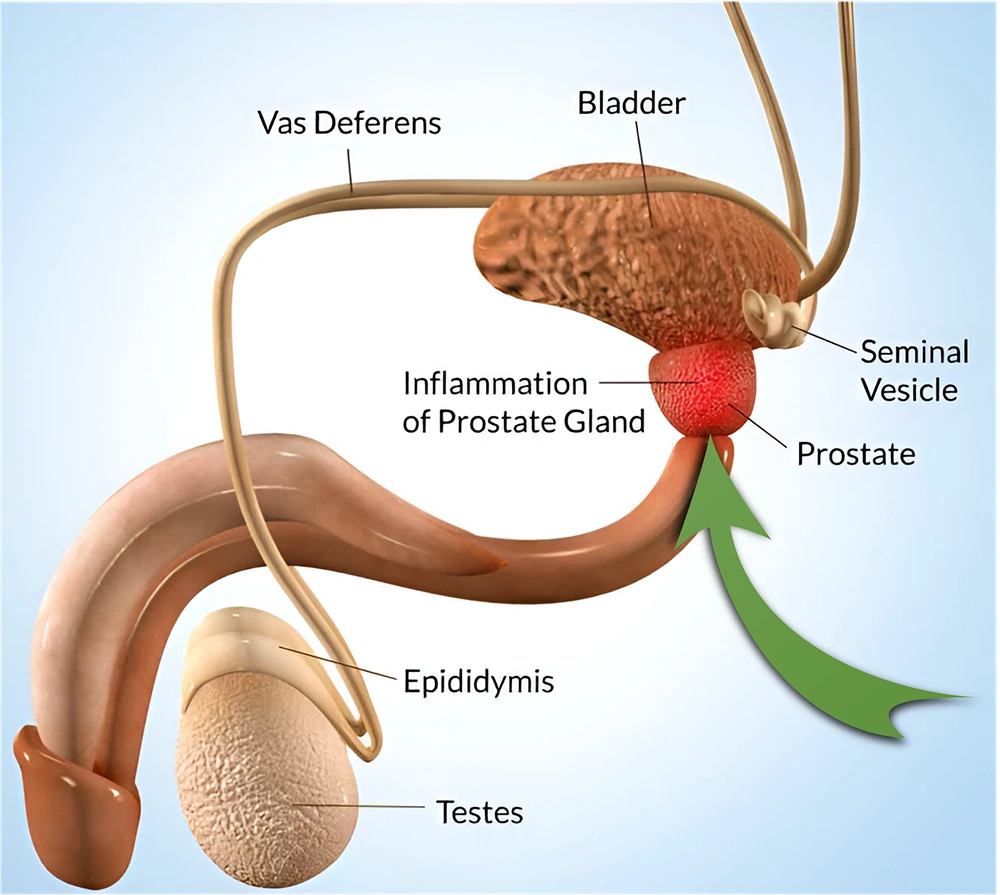
About the Prostate Gland:
The prostate gland is a walnut-shaped male organ that produces prostatic fluid, which aids in sperm transportation during ejaculation. It surrounds the urethra, through which urine and semen pass out of the body.
What is Enlarged Prostate?
Enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or benign prostatic enlargement (BPE), refers to the condition where the prostate gland becomes larger. This typically occurs in men as they age, especially after the age of 50.
Causes of Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate
Understanding Prostate Health
Risk of Prostate Cancer
Enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is characterized by an increase in the size of the prostate gland. Contrary to prostate cancer, which is a separate condition, BPH itself does not elevate the risk of developing prostate cancer. While it’s possible for a person to have both conditions simultaneously, they typically originate from different areas within the prostate gland and require distinct management approaches.
Effects of Enlarged Prostate
The impact of an enlarged prostate varies widely among individuals. For some men, particularly those with mild enlargement, symptoms may be minimal and not necessitate active treatment. However, for others, an enlarged prostate can lead to bothersome urinary symptoms that significantly affect daily life. Common symptoms include:
- Weak Flow during Urination: Difficulty starting to urinate or experiencing a weak urinary stream.
- Incomplete Emptying of the Bladder: A sensation that the bladder has not completely emptied after urination.
- Difficulty Initiating Urination: Struggling to begin urination despite feeling the urge.
- Post-void Dribbling: Urine leakage or dribbling immediately after finishing urination.
- Increased Urinary Frequency: Needing to urinate more frequently, particularly at night (nocturia).
- Urinary Urgency: Sudden, urgent need to urinate that may lead to leakage if not reached in time. In rare cases, blood in the urine (hematuria) may also occur, indicating a need for medical evaluation.
Diagnosis of Enlarged Prostate
If symptoms suggestive of an enlarged prostate are present, diagnosis typically involves:
- Personal and Family Medical History: Understanding any past medical conditions and family history of prostate issues.
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination, including a digital rectal exam (DRE), to assess the size, shape, and condition of the prostate gland.
- Medical Tests: These may include urine tests to rule out infections or other conditions, as well as imaging studies such as ultrasound or uroflowmetry to assess urine flow rate and volume.
Treatment Options of Enlarged Prostate
The approach to managing an enlarged prostate depends on the severity of symptoms, their impact on quality of life, and individual patient preferences. Treatment options include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Recommendations may include reducing fluid intake before bedtime, limiting caffeine and alcohol consumption, and practicing pelvic floor exercises (Kegel exercises).
- Medications: Various medications can help alleviate symptoms by reducing prostate size (alpha-blockers, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors), relaxing bladder muscles (anticholinergics), or addressing inflammation (NSAIDs).
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Techniques such as transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT), transurethral needle ablation (TUNA), or laser therapy may be used to shrink or remove excess prostate tissue.
- Surgical Interventions: In cases where symptoms are severe or medications and minimally invasive procedures have been ineffective, surgical options like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or laser prostatectomy may be recommended to remove obstructive prostate tissue.
Monitoring and Follow-Up of Enlarged Prostate
For individuals with mild symptoms or those opting for watchful waiting, regular follow-up visits with a urologist are essential to monitor prostate health and symptom progression. This approach ensures timely intervention if symptoms worsen or complications arise.
In summary, while an enlarged prostate is a common condition affecting many men as they age, its impact on daily life can vary significantly. Early recognition of symptoms and appropriate medical evaluation are crucial for determining the most suitable treatment approach and optimizing long-term prostate health and quality of life.
Get Expert Help Today
Don’t let an enlarged prostate disrupt your life. Reach out to Max Stone & Surgical Center – Max Hospital Faridabad – for a thorough consultation & a personalized treatment plan. Our skilled team is dedicated to providing exceptional care and support. Schedule your appointment today & take the first step towards a healthier, more comfortable future.


Get a Call for Appointment
Fill out this form to receive a call from us and schedule your appointment. Start your journey to better health with our expert care today!
